|
[ Hit a button for Quick Look!! ] |
    
|
|
Among them, angina and myocardial infarction are particularly important and attracting attention as heart diseases closely related to lifestyle-related diseases. |
|
[ Hit a button for Quick Look!! ] |
    
|
|
Among them, angina and myocardial infarction are particularly important and attracting attention as heart diseases closely related to lifestyle-related diseases. |
|
A dedicated blood vessel for working the heart surrounds the heart and is called a coronary artery.
The direct cause of angina is arteriosclerosis of the coronary arteries. The cause of arteriosclerosis is certainly the effect of aging, but the most important cause is improper lifestyle. |

|
|
|
|
[ A disease called Angina ] |
|
|
What kind of disease is angina |
The heart itself also needs oxygen and nutrients as an organ. The blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle that functions the heart are called coronary arteries.
An angina attack occurs when a person with arteriosclerosis in the coronary arteries is stressed by sudden exercise, strong stress, or bathing in a hot bath. |

|
|
|
|
[ Symptom of Angina ] |
||||||
|
Typical symptoms |
The characteristic symptom of angina is that severe chest pain suddenly strikes and the pain lasts for a few seconds to 15 minutes and then disappears spontaneously. The degree of pain varies from mild to severe, and patients complain of chest tightness. It can be very painful and cold sweaty.
|
|||||
|
Types of angina |
There are five types of angina:
|
|||||

|
|
|
|
[ Cause of Angina ] |
|
|
Causes of angina |
A direct cause of ischemic heart disease such as angina and myocardial infarction is coronary atherosclerosis. |

|
|
|
|
[ Diagnosis of Angina ] |
|
|
How to diagnose angina |
There are two types of heart disease tests: general tests that are performed in daily preventive medical examinations, and urgent tests that are performed due to the occurrence of seizures. 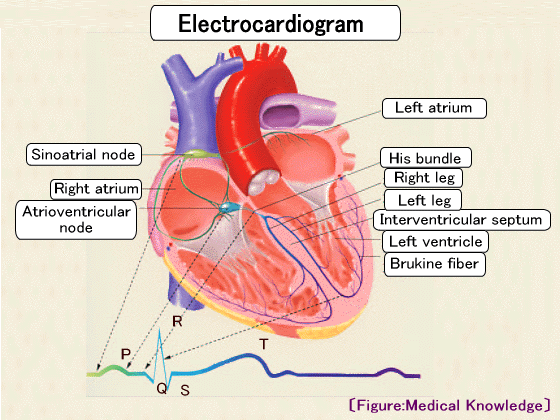
In electrocardiography, three waveforms, P wave, QRS wave, and T wave, are measured. The P wave indicates the electrical excitement of the atrium, and the QRS complex indicates the electrical excitement of the ventricles. The T wave is the waveform when the electrical excitement of the ventricles is restored. |

|
|
|
|
[ Treatment of Angina ] |
|
|
Treatment policy for angina |
In order to prevent ischemic heart disease such as angina pectoris and myocardial infarction, it is necessary to keep in mind a modest daily life and pay attention to the following points. |
|
Drug therapy |
As drug therapy, the following drugs are used according to the symptoms. |
|
Treatment with catheter |
The treatment method using a catheter is to insert a small balloon with a diameter of 2 to 4 mm and a length of about 20 mm into the lesion of the damaged and narrowed coronary artery, which is the direct cause of angina and myocardial infarction, and inflate the coronary artery. It is a method of expanding from the inside. |
|
Surgery |
More severely ill patients require extensive surgical treatment called coronary artery bypass surgery. |